Flare system holds a pivotal position within the manufacturing industry. Delve into an in-depth exploration of its structure and operating principles in VHE‘s article.
In mining rigs, refineries, and petrochemical plants, tall fire towers are often observed burning. The flare system is utilized as an exhaust treatment system in chemical, oil, and gas extraction processes. Structurally, they are recognized as a burning platform and are typically positioned at a height of approximately 20-30 meters above the ground, occasionally exceeding 50 to 60 meters in height (Peteco).
Additionally, this system finds applications in various other scenarios like managing emissions from landfills, paper mills, or food factories.
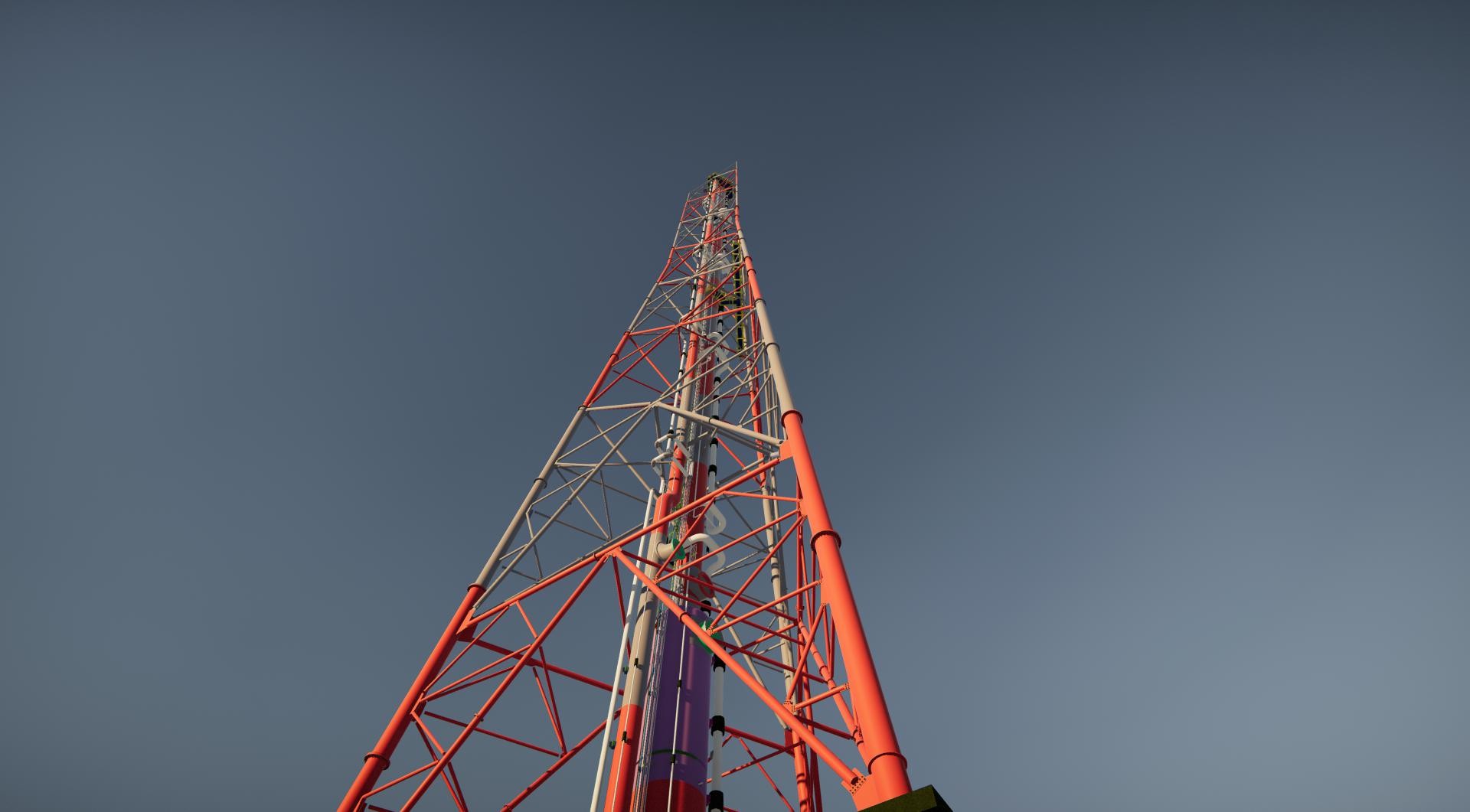

The Flare System typically consists of two main parts:
Lower part: This section includes the supporting tower truss known as the Stack (for vertical trusses) and the Boom (for horizontal or inclined trusses). It is primarily constructed using U- and V-shaped structural steel bars interconnected. Tubes located in the center of the coal or beneath the body lead up to the main torch.
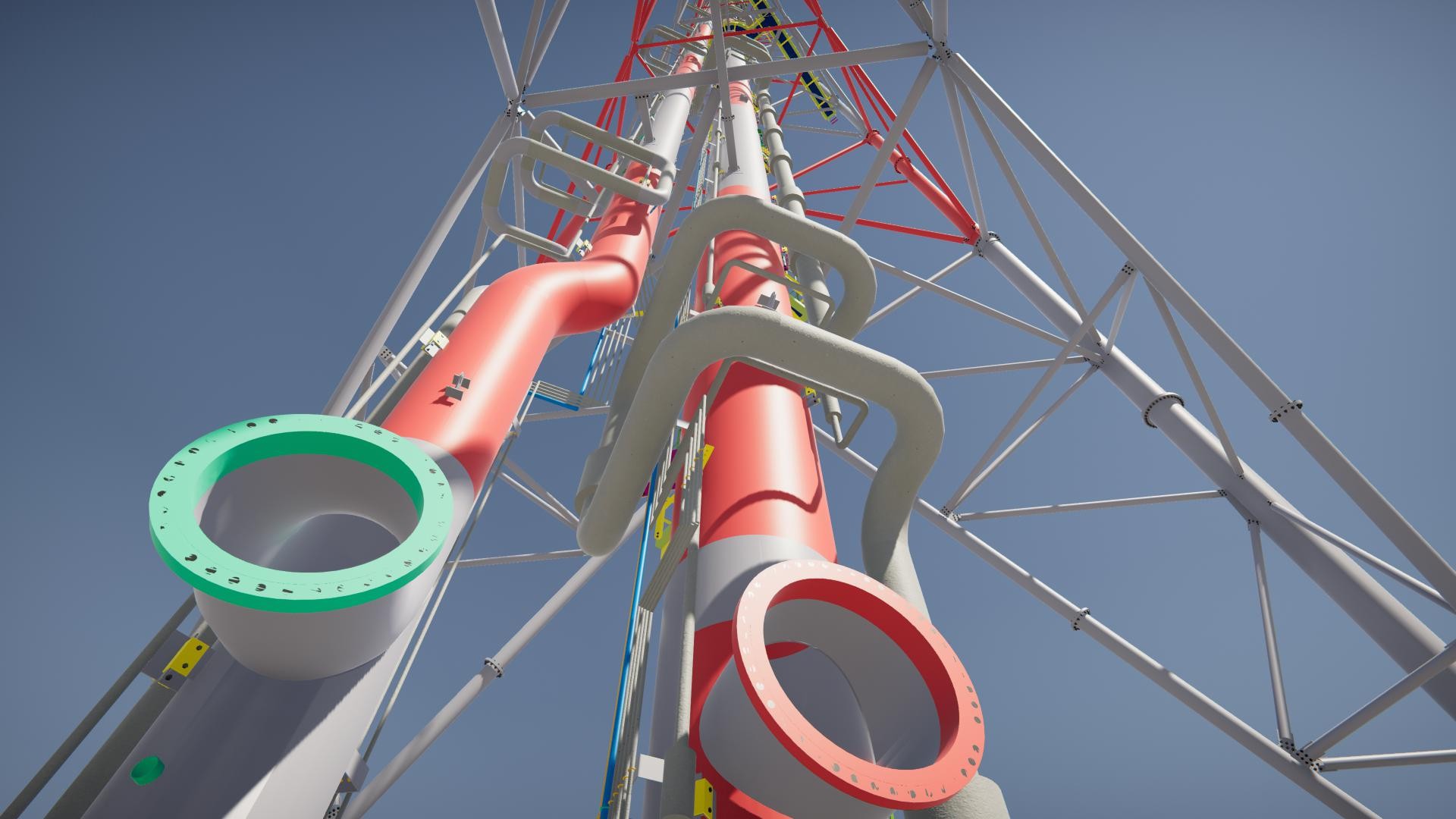

Flare Tip: serves as an integral component within flare systems, playing a vital role in emission control. Typically designed with a vertical or angled tubular structure, it consists of multiple smaller tubes organized in a bundle. Flare tips are often crafted from high-temperature-resistant materials such as stainless steel to withstand the intense heat and pressure generated during emission combustion. The dimensions of each flare tip are customized to match the particular emission flow rate it is intended to manage. Elevated flare tip and ground flare tip are the two most prevalent designs employed in flare systems.
- Elevated flare tips, mounted at elevated heights, are typically utilized in industrial facilities and drilling platforms with substantial emission volumes.
- Conversely, ground flare tips are installed on the ground and are commonly employed in facilities and platforms handling smaller emission flows.
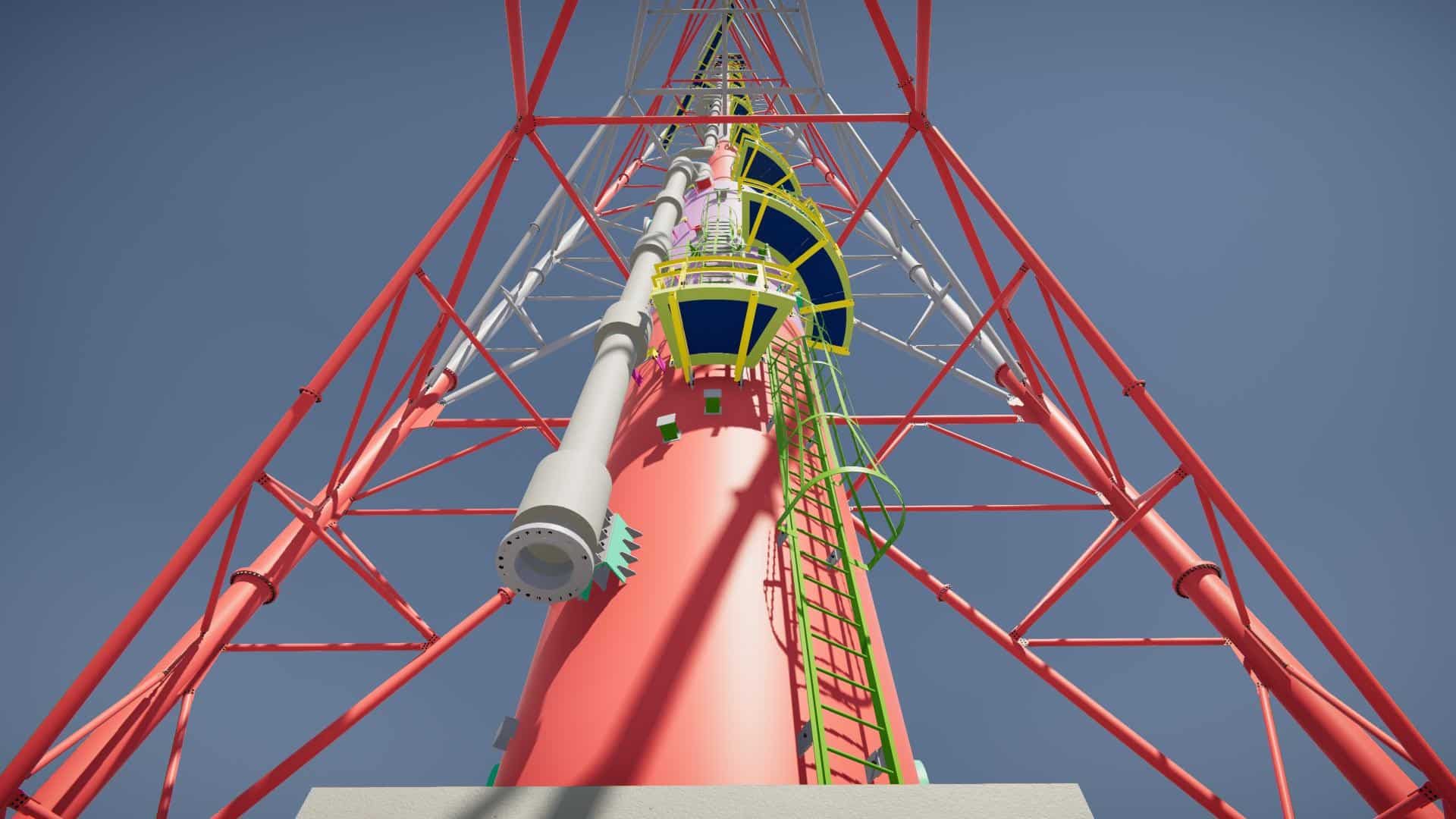

III. System Operating Principle:
The Flare system functions by safely burning excess gases and toxic emissions during production activities.
Basic Operation Steps of the Flare System:
- Gas Collection: Gather exhaust gas from various sources like tanks, gas pipelines, and pressure relief valves.
- Initial Treatment: Before entering the flare system, impurities such as dirt, water, or corrosive substances can undergo pretreatment.
- Combustion: Direct the gas into the combustion chamber of the flare, where the ignition system sparks high-temperature combustion.
- Purification: Through combustion, organic pollutants are eliminated, and exhaust gases are detoxified, transforming into safer byproducts like carbon dioxide, water, or heat.
- Emission: The combustion products are released into the environment through the flare chimney. The design of the chimney ensures the dispersion of exhaust gas widely, reducing its impact on the environment.